Pill with imprint 215 is Yellow, Capsule/Oblong and has been identified as Gabapentin 300 mg. It is supplied by Ascend Laboratories, LLC.
Gabapentin is used in the treatment of Back Pain; Postherpetic Neuralgia; Epilepsy; Chronic Pain; Seizures and belongs to the drug class gamma-aminobutyric acid analogs. Risk cannot be ruled out during pregnancy. Gabapentin 300 mg is not a controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act (CSA).
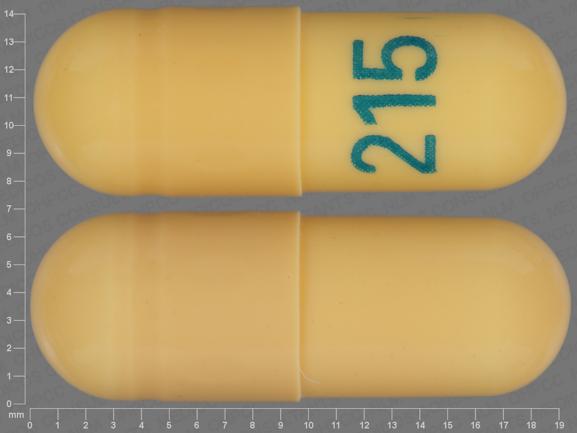
Gabapentin 300mg
- Imprint
- 215
- Strength
- 300 mg
- Color
- Yellow
- Size
- 19.00 mm
- Shape
- Capsule/Oblong
- Availability
- Prescription only
- Drug Class
- Gamma-aminobutyric acid analogs
- Pregnancy Category
- C – Risk cannot be ruled out
- CSA Schedule
- Not a controlled drug
- Labeler / Supplier
- Ascend Laboratories, LLC
- Inactive Ingredients
- corn starch, lactose anhydrous, magnesium silicate, gelatin, sodium lauryl sulfate, titanium dioxide, ferric oxide yellow
Note: Inactive ingredients may vary.
Labelers / Repackagers
| NDC Code | Labeler / Repackager |
|---|---|
| 67877-0223 | Ascend Laboratories LLC |
| 16714-0504 | NorthStar Rx LLC |
I Want to Buy Gabapentin, What Should I know Before I see A doctor ?
If you’re considering gabapentin, it’s important to consult with a doctor beforehand. Here are some key points to consider before your appointment:
- Medical History: Be prepared to discuss your medical history with your doctor, including any past or current conditions, medications you’re taking, and any allergies you may have.
- Reason for Use: Be ready to explain why you believe gabapentin may be necessary for your health. Whether it’s for epilepsy, neuropathic pain, or another condition, your doctor will need to understand your symptoms and medical needs.
- Potential Side Effects: Familiarize yourself with the potential side effects of gabapentin. These can include dizziness, drowsiness, and coordination problems. Understanding the possible risks can help you make an informed decision.
- Interactions: Gabapentin can interact with other medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Make sure to inform your doctor of all medications you’re taking to avoid any potential interactions.
- Dosage and Administration: Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage of gabapentin based on your condition and medical history. Be prepared to discuss dosing instructions and how to take the medication correctly.
- Monitoring: Your doctor may recommend regular check-ups to monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan if necessary. It’s important to follow up with your doctor as directed to ensure the medication is working effectively and safely.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: If you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding, discuss this with your doctor. Gabapentin may not be suitable during pregnancy or while breastfeeding, and your doctor can advise you on the best course of action.
- Alternative Treatments: Explore alternative treatments or therapies that may be available for your condition. Your doctor can help you weigh the benefits and risks of gabapentin compared to other options.
By discussing these points with your doctor, you can ensure that gabapentin is the right choice for you and that you understand how to use it safely and effectively.