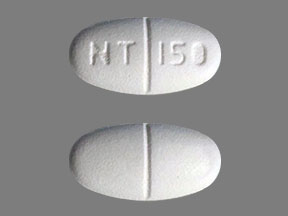
Pill with imprint NT 150 is White, Oval and has been identified as Gabapentin 600 mg. It is supplied by Solco Healthcare U.S., LLC.
Gabapentin is used in the treatment of Back Pain; Postherpetic Neuralgia; Epilepsy; Chronic Pain; Seizures and belongs to the drug class gamma-aminobutyric acid analogs. Risk cannot be ruled out during pregnancy. Gabapentin 600 mg is not a controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act (CSA).
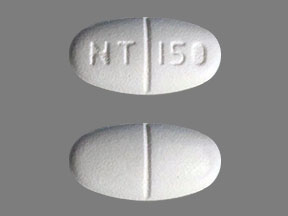
Gabapentin
- Imprint
- NT 150
- Strength
- 600 mg
- Color
- White
- Shape
- Oval
- Availability
- Prescription only
- Drug Class
- Gamma-aminobutyric acid analogs
- Pregnancy Category
- C – Risk cannot be ruled out
- CSA Schedule
- Not a controlled drug
- Labeler / Supplier
- Solco Healthcare U.S., LLC
- Manufacturer
- ScieGen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- National Drug Code (NDC)
- 43547-0332 (Discontinued)
- Inactive Ingredients
- copovidone, hydroxypropyl cellulose, magnesium stearate, mannitol, poloxamer 407, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, magnesium silicate, titanium dioxide
What is Gabapentin ?
Gabapentin is a medication used to treat seizures (epilepsy) and nerve pain (neuropathic pain). It belongs to a class of medications called anticonvulsants or antiepileptic drugs.
What does Gabapentin can do ?
- Seizure Management: Gabapentin may be used alongside other medications to reduce seizure frequency in adults and children aged three and older who experience partial-onset seizures.
- Postherpetic Neuralgia: In adults, gabapentin is effective for managing postherpetic neuralgia, which is persistent nerve pain following a Shingles infection.
- Horizant (Gabapentin Enacarbil): This long-acting prodrug of gabapentin is taken once daily, usually around 5 PM, to relieve restless legs syndrome (RLS) or nerve pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia.
- Generic Availability: Gabapentin is available in generic forms, though not all generics are interchangeable with some branded versions.
- Off-Label Uses: Gabapentin may also be prescribed off-label for conditions such as fibromyalgia, persistent hiccups, migraine prevention, and hot flashes. Different brands and formulations of gabapentin exist, each with specific uses and dosing instructions.
- Neurontin: Used to treat pain from shingles (postherpetic neuralgia) and, when combined with other seizure medications, treats partial-onset seizures in adults and children over three years old.
- Gralise: Specifically designed for treating postherpetic neuralgia and should not be used for other conditions.
- Horizant: An extended-release tablet intended for restless legs syndrome and postherpetic neuralgia.
- Generic Gabapentin Capsules: Used for treating postherpetic neuralgia and as an additional therapy for partial-onset seizures in adults and children over three years old.
Here’s a rundown of precautions, side effects, and how to take gabapentin:
Precautions:
- Allergies: Inform your doctor if you have any allergies to gabapentin or any other medications.
- Medical History: Disclose your medical history to your doctor, especially if you have a history of kidney disease, mood disorders (such as depression or bipolar disorder), substance abuse, or breathing problems.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Inform your doctor if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding, as gabapentin may pose risks to the fetus or infant.
- Driving and Operating Machinery: Gabapentin may cause dizziness, drowsiness, or blurred vision, which can impair your ability to drive or operate machinery. Use caution when engaging in activities that require mental alertness until you know how gabapentin affects you.
- Alcohol and Sedatives: Avoid consuming alcohol or taking sedative medications while using gabapentin, as it can increase the risk of drowsiness and dizziness.
- Withdrawal: Do not stop taking gabapentin suddenly without consulting your doctor, as this can lead to withdrawal symptoms such as seizures, anxiety, insomnia, nausea, or sweating.
Side Effects:
Common side effects of gabapentin may include:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Nausea
- Blurred vision
- Dry mouth
- Weight gain
- Tremors
- Difficulty speaking
- Memory problems
Less common but more serious side effects may include:
- Suicidal thoughts or behavior
- Mood changes (such as depression or anxiety)
- Swelling of the hands, feet, or ankles
- Rapid weight gain
- Signs of infection (such as fever or sore throat)
- Unusual bruising or bleeding
- Severe skin reactions (such as rash, blistering, or peeling)
If you experience any severe or persistent side effects while taking gabapentin, contact your doctor immediately.
What Are the Risks of Taking Gabapentin ?
If you are between the ages of 18 and 60, take no other medications, and have no other medical conditions, you are more likely to experience the following side effects with gabapentin:
- Common Side Effects: Dizziness, drowsiness, tiredness, fever, and nystagmus (rapid, uncontrollable eye movements). Gabapentin-induced drowsiness can impair your ability to drive or operate machinery. Alcohol and other sedatives can enhance this effect.
- Behavioral Changes in Children: When used to treat epilepsy in children aged three to twelve, gabapentin may cause behavioral problems, hostility, aggression, or thought disturbances.
- Other Side Effects: Blurred vision, amblyopia (lazy eye), dry mouth, peripheral edema (fluid retention in feet and hands), tremor, sexual dysfunction, and gastrointestinal disturbances.
- Titration: Gabapentin should be titrated up slowly to reduce the risk of side effects, although this may delay the onset of its effects.
- Mental Health Risks: Similar to other anticonvulsants, gabapentin may increase the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts, especially in young adults under 24.
- Discontinuation Syndrome: Abruptly stopping gabapentin can cause withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, insomnia, nausea, pain, and sweating. It should be tapered off slowly under medical supervision.
- Kidney Disease: The dosage needs to be reduced for individuals with kidney disease.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Rarely, hypersensitivity reactions can occur, including fever, rash, swollen lymph nodes, swollen facial features, or throat swelling.
- Drug Interactions: Gabapentin may interact with other medications, including antacids, hydrocodone, morphine, and other sedatives, potentially causing increased sedation or dizziness. It may also cause false-positive results on some urinary protein tests.
- Misuse and Abuse: There have been reports of gabapentin misuse and abuse, especially in individuals with a history of drug abuse.
- Administration: Gabapentin typically requires three times daily administration due to its short duration of effect. However, gabapentin enacarbil (brand name Horizant) is a long-acting prodrug that only requires once-daily dosing.
- Seizure Disorders: Gabapentin is only effective for partial-onset seizures and not for other types of seizure disorders.
- Interchangeability: Some branded and generic forms of gabapentin are not interchangeable.
Mechanism of Action
Gabapentin is a medication that is primarily used to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Its exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is known to interact with certain components of the nervous system. Gabapentin works primarily by binding to the α2δ subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels, which leads to a reduction in calcium influx and a subsequent decrease in the release of excitatory neurotransmitters. This action helps to stabilize neuronal activity and reduce symptoms of seizures and neuropathic pain. Although its exact mechanism is not fully understood, gabapentin’s effects on neurotransmission and neuronal excitability make it a valuable medication for a variety of neurological and pain-related conditions.
Here is a detailed explanation of the proposed mechanisms by which gabapentin exerts its therapeutic effects:
Mechanism of Action
- Binding to the α2δ Subunit of Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels:
- Gabapentin binds with high affinity to the α2δ subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system.
- This binding inhibits the influx of calcium ions into neurons, which in turn reduces the release of excitatory neurotransmitters such as glutamate, norepinephrine, and substance P.
- By decreasing the release of these neurotransmitters, gabapentin helps to stabilize neuronal activity and reduce the hyperexcitability that contributes to seizures and neuropathic pain.
- Reduction of Excitatory Neurotransmission:
- The inhibition of calcium influx and subsequent reduction in neurotransmitter release results in decreased excitatory synaptic transmission.
- This reduction in excitatory signaling is believed to contribute to the anticonvulsant and analgesic effects of gabapentin.
- Modulation of GABAergic Neurotransmission:
- Although gabapentin is structurally similar to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), it does not directly bind to GABA receptors or influence GABA synthesis or uptake.
- However, gabapentin may enhance the synthesis of GABA and increase its release in certain brain regions, which could contribute to its overall calming effect on neuronal activity.
- Inhibition of Central Sensitization:
- In conditions like neuropathic pain, there is often a phenomenon known as central sensitization, where the nervous system becomes sensitized to pain stimuli.
- By inhibiting calcium influx and reducing excitatory neurotransmitter release, gabapentin helps to diminish central sensitization and alleviate chronic pain symptoms.
Therapeutic Effects
- Anticonvulsant:
- Gabapentin’s ability to decrease neuronal excitability and stabilize electrical activity in the brain makes it effective in controlling seizures, particularly partial seizures.
- Analgesic:
- The reduction in neurotransmitter release and inhibition of central sensitization make gabapentin effective in treating various forms of neuropathic pain, such as diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia.
- Other Uses:
- Gabapentin is also used off-label for other conditions like restless legs syndrome (RLS) and certain anxiety disorders, where its modulatory effects on the nervous system can provide symptomatic relief.
How to Take Gabapentin:
- Dosage: Take gabapentin exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Do not adjust your dosage without consulting your doctor first.
- Administration: Gabapentin is usually taken orally with or without food. Swallow the capsule or tablet whole with a full glass of water.
- Timing: Take gabapentin at the same times each day to maintain a consistent level of the medication in your body.
- Gradual Dosing: If you are starting gabapentin treatment or increasing the dosage, your doctor may recommend starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it over time to minimize side effects.
- Duration of Treatment: Continue taking gabapentin for the full duration of treatment prescribed by your doctor, even if you start to feel better.
- Storage: Store gabapentin at room temperature away from moisture and heat. Keep it out of reach of children and pets.
ScieGen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
ScieGen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. is a key player in the generic pharmaceutical industry, known for its commitment to quality, innovation, and affordability. With a strong focus on research and development, regulatory compliance, and strategic growth, ScieGen continues to expand its presence in the U.S. and international markets. The company’s dedication to sustainable practices and corporate responsibility further underscores its role as a responsible and forward-thinking pharmaceutical provider.
ScieGen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. is a pharmaceutical company that specializes in the development, manufacturing, and marketing of generic prescription medications. Here’s an overview of ScieGen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.:
Company Overview
- Establishment and Headquarters:
- Founded: ScieGen Pharmaceuticals was established to provide high-quality generic pharmaceuticals.
- Headquarters: Hauppauge, New York, USA.
- Operations and Facilities:
- Manufacturing: ScieGen operates manufacturing facilities that comply with stringent regulatory standards. The company’s facilities are designed to support the production of a wide range of dosage forms, including tablets, capsules, and powders.
- Research and Development: The company focuses on R&D to develop new generic formulations and improve existing ones, ensuring they meet the highest quality standards.
Product Portfolio
- Generics:
- Therapeutic Areas: ScieGen offers a broad range of generic medications across various therapeutic categories, including cardiovascular, central nervous system, gastrointestinal, anti-infective, and pain management drugs.
- Dosage Forms: The company manufactures various dosage forms, such as tablets, capsules, and oral solutions.
Key Areas of Operation
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Quality Assurance: ScieGen adheres to rigorous quality control measures and regulatory requirements set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and other global regulatory bodies.
- GMP Compliance: The company ensures that its manufacturing processes comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to guarantee the safety, efficacy, and quality of its products.
- Research and Development:
- Innovation: ScieGen invests in R&D to develop cost-effective generic alternatives to brand-name drugs, focusing on complex generics and niche therapeutic areas.
- Pipeline: The company has a robust pipeline of products in various stages of development, aimed at expanding its market presence and addressing unmet medical needs.
- Manufacturing Excellence:
- Advanced Technology: ScieGen’s manufacturing facilities are equipped with advanced technology to produce high-quality pharmaceuticals efficiently.
- Capacity: The company’s facilities have significant production capacities to meet both domestic and international demand.
Strategic Growth
- Market Strategy:
- Product Launches: ScieGen focuses on the timely launch of generic medications to capture market share and provide affordable options to patients.
- Competitive Pricing: The company’s competitive pricing strategy ensures that its products are accessible to a broad patient population.
- Partnerships and Collaborations:
- Expansion: ScieGen pursues strategic partnerships and collaborations to enhance its product offerings and expand its market reach.
- Distribution Networks: The company has established robust distribution networks to ensure the widespread availability of its products.
Corporate Responsibility
- Sustainability:
- Environmental Practices: ScieGen is committed to sustainable manufacturing practices, focusing on minimizing its environmental impact through efficient resource use and waste management.
- Community Engagement:
- CSR Activities: The company engages in corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives aimed at improving healthcare access, supporting education, and contributing to community development.
Medications for Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a brain disorder involving recurrent seizures. Anti-seizure medications can help prevent or stop seizures. The choice depends on the type of seizure, the age of the person, the potential side effects of the medication, other medications they may be taking, or concurrent health conditions.
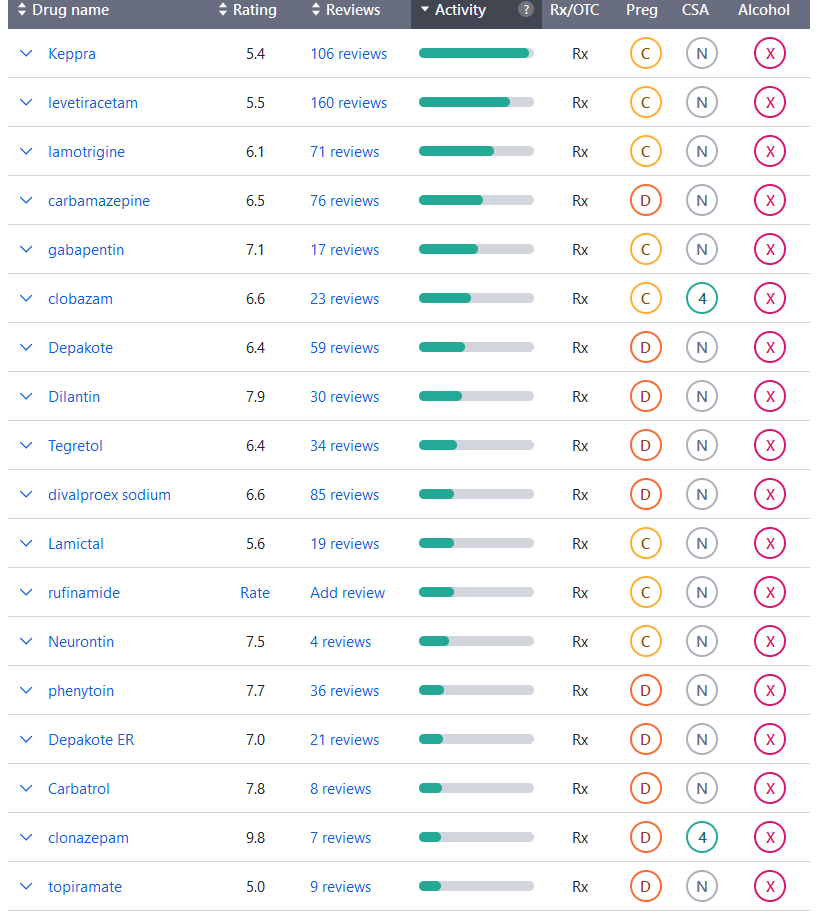
Various seizure types
- Acetazolamide (Diamox)
- Clobazam (Onfi)
- Clonazepam (Klonopin)
- Clorazepate (Tranxene)
Key Points of Taking Gabapentin
If you are between the ages of 18 and 60, take no other medications, and have no other medical conditions, you are more likely to experience the following side effects with gabapentin:
- Common Side Effects: Dizziness, drowsiness, tiredness, fever, and nystagmus (rapid, uncontrollable eye movements). Gabapentin-induced drowsiness can impair your ability to drive or operate machinery. Alcohol and other sedatives can enhance this effect.
- Behavioral Changes in Children: When used to treat epilepsy in children aged three to twelve, gabapentin may cause behavioral problems, hostility, aggression, or thought disturbances.
- Other Side Effects: Blurred vision, amblyopia (lazy eye), dry mouth, peripheral edema (fluid retention in feet and hands), tremor, sexual dysfunction, and gastrointestinal disturbances.
- Titration: Gabapentin should be titrated up slowly to reduce the risk of side effects, although this may delay the onset of its effects.
- Mental Health Risks: Similar to other anticonvulsants, gabapentin may increase the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts, especially in young adults under 24.
- Discontinuation Syndrome: Abruptly stopping gabapentin can cause withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, insomnia, nausea, pain, and sweating. It should be tapered off slowly under medical supervision.
- Kidney Disease: The dosage needs to be reduced for individuals with kidney disease.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Rarely, hypersensitivity reactions can occur, including fever, rash, swollen lymph nodes, swollen facial features, or throat swelling.
- Drug Interactions: Gabapentin may interact with other medications, including antacids, hydrocodone, morphine, and other sedatives, potentially causing increased sedation or dizziness. It may also cause false-positive results on some urinary protein tests.
- Misuse and Abuse: There have been reports of gabapentin misuse and abuse, especially in individuals with a history of drug abuse.
- Administration: Gabapentin typically requires three times daily administration due to its short duration of effect. However, gabapentin enacarbil (brand name Horizant) is a long-acting prodrug that only requires once-daily dosing.
- Seizure Disorders: Gabapentin is only effective for partial-onset seizures and not for other types of seizure disorders.
- Interchangeability: Some branded and generic forms of gabapentin are not interchangeable.